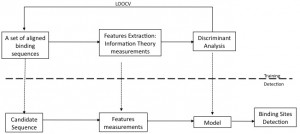
Sequence Information Gain based Motif Analysis (SIGMA) is a novel methodology based on information theoretic metrics for finding regulatory sequences in promoter regions. This new approach aims at a trade-off between the good generalisation properties of pure entropy methods and the ability to position-dependency metrics to improve detection power.
This methodology has been tested on genomic sequence data for Homo sapiens and Mus musculus. SIGMA has been compared with different publicly available alternatives for motif detection, such as MEME/MAST, and previous work such Qresiduals projections or information theoretic based detectors.
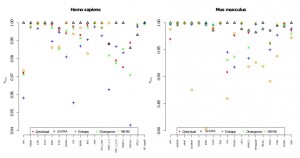
Performance of each algorithm is shown through AUC for a set of TFBS for the Homo sapiens and Mus musculus organisms.
Information theoretic based detectors and Qresiduals can be found MEET R-package which is available as a contributed package from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN).